| test method |
|
|
|
|
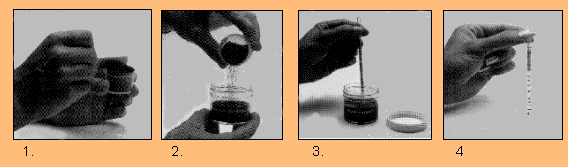
Elcometer 134A Chloride Kit for Abrasives, Soil and Concrete Need 1: Abrasives As you are aware, most surface contaminants - rust, dirt etc - on a surface will be removed during the blasting of the materials, to a specified profile. The abrasive material used is often an expensive consumable. As this is the case, and because the abrasive can be re-used, contractors regularly recycle abrasives two or three times. Abrasive disposal is also extremely expensive. However, as the abrasive is also removing any contaminants, these contaminants will be included in the abrasive being re-blasted onto the metal. This includes the chloride contaminants that you are attempting to remove in the first case by blasting. It is therefore imperative, that the customer is aware of the level of chloride in the abrasive. Need 2: Soil Contamination Pipelines and other steel structures, once coated, are open to the elements. Coatings subjected to a high concentration of chloride ion will fail faster than a coating in a much lower concentration. It is therefore important, especially where the structure is to be buried, or partially buried, for the contractor to be able to quickly establish the chloride concentration of the soil. The Elcometer 134A is a simple field test that can be used to accurately measure the chloride concentration in blast media or soils. Need 3: Concrete Contamination In many parts of the world, salt or rock salt is used on roads to reduce ice build up. As concrete is porous, this contaminated melting water will be drawn into the concrete thereby increasing the speed of corrosion of the reinforcement bars (rebars). To this end, urethane liners and epoxy coatings are applied to concrete structures (bridges etc) as a barrier coat. Moreover, when the concrete is mixed, if the water used is high in salts, as the concrete is porous, the water mixes with the soluble salts and can cause increased corrosion rates for the rebar. This need is something for all Concrete Structural Engineers to consider when constructing buildings, pipelines, bridges etc. Easy Operation The Elcometer 134A uses a similar test method to the 134 Surface test.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||